Wikipedia (But Better)
Product Design, UX Research, UI Design, User Testing
Concept redesign of Wikipedia to challenge perceptions that it is not a trustworthy source of information, enhance credibility, and build trust among users.
the BRIEF
With the recent proliferation of misinformation online, the trustworthiness of information is under scrutiny like never before. For over 20 years, Wikipedia has led the movement of free and open information online, not only reshaping the internet but empowering billions of users worldwide to access, contribute to, and benefit from a wealth of freely available knowledge. Yet Wikipedia seems tainted by the question of trustworthiness. Through this project, I set out to change Wikipedia’s reputation by enhancing credibility and confidence in the eyes of its users.
Duration
12 Weeks
Type
Student Project
Tools
the OUTCOME
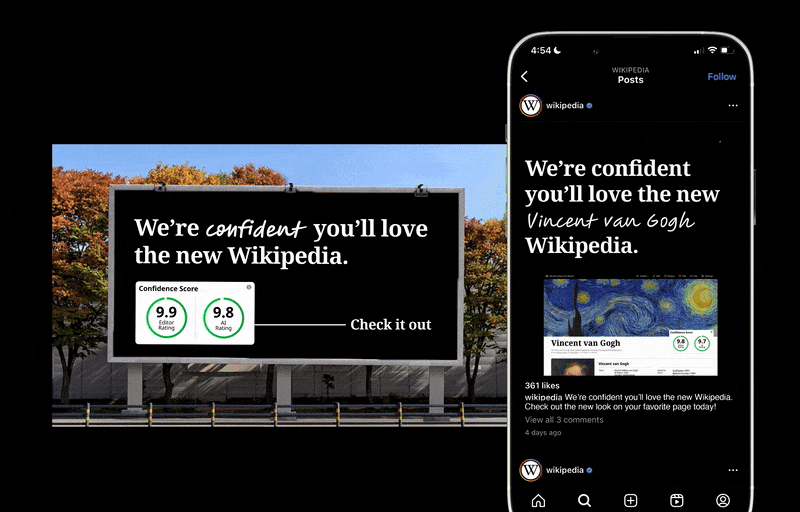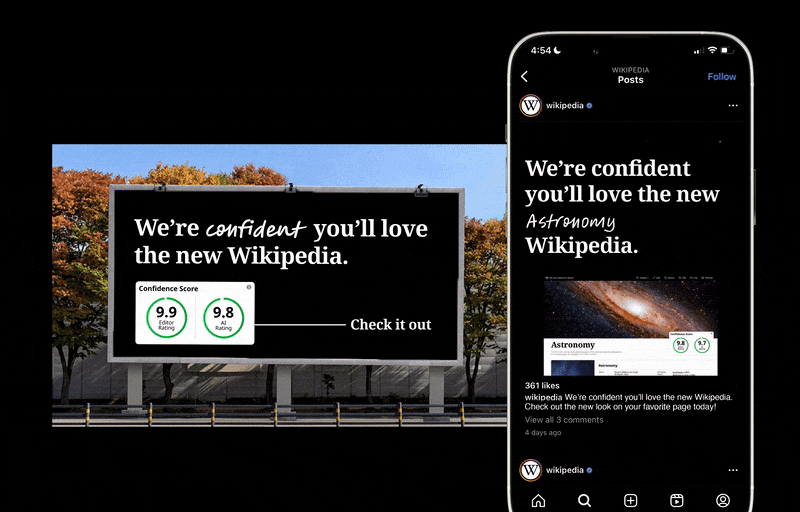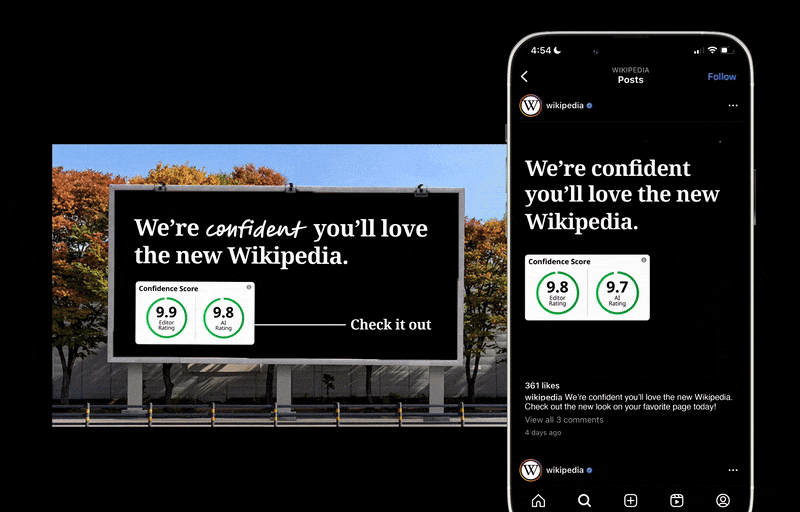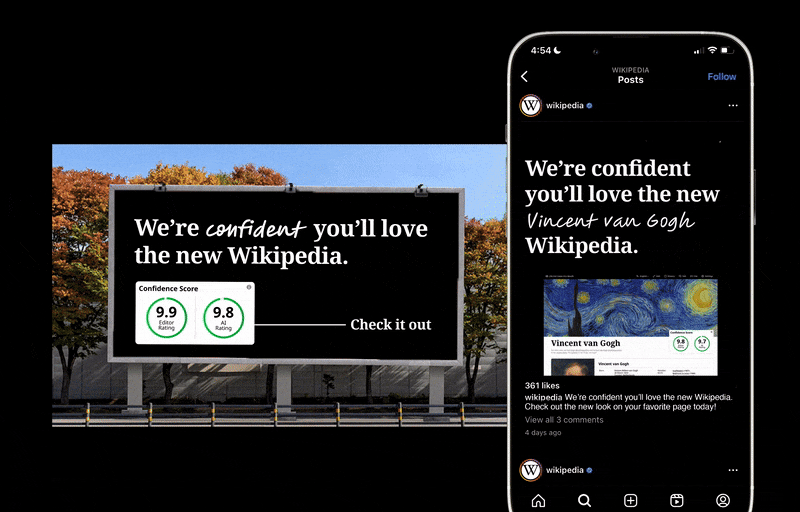
Wikipedia feels shady because users don’t have a way to evaluate the accuracy of information in articles. With my concept redesign for Wikipedia, I implemented a new Confidence Score feature that allows users to assess an article’s accuracy at a glance. In user testing, 100% of respondents said having the new Confidence Score feature on articles made Wikipedia more trustworthy. See my entire process below!
the PROCESS
ASSUMPTION
Wikipedia is failing because it feels shady.
When visiting Wikipedia articles, users are often confronted with flags or pop-ups showing that the article’s accuracy is questionable. This, combined with the concerns of anyone being able to edit information and being constantly pestered to donate money, all add to the perception that Wikipedia isn’t a reliable source of information.
Looks like this…
But feels like this.
VALIDATING ASSUMPTIONS
In order to explore my assumption, I conducted a four question survey to gain insights into users’ current perception of Wikipedia.
Key Takeaways:
Most respondents (62%) do not think Wikipedia is generally a reliable source of information
When ranking how trustworthy Wikipedia was on a scale of 1 (not at all trustworthy) to 10 (very trustworthy), the average answer was 5.3 out of 10 → if this were a letter grade, Wikipedia is failing
Among users who said Wikipedia was a reliable source of information, the average rating was 7.5 out of 10 → even users who do trust Wikipedia still have doubts
The most common reason for not trusting information on Wikipedia was because “anyone has the ability to edit information” → users want accountability for who is editing Wikipedia articles
In order to trust Wikipedia, users want information to be verified or reviewed → users want something that validates their trust
Quotes from survey responses
THESIS
In order to be seen as a reputable, trustworthy source of information, Wikipedia needs to verify information accuracy within articles.
USER STORIES
As a Wikipedia user, I want to easily identify articles with verified, fact-checked information, so that I can feel confident about its credibility.
As a Wikipedia contributor, I want to correct factual inaccuracies and update articles to ensure that all readers have access to the correct information.
As a member of the general public, I want to know that Wikipedia thoroughly reviews articles for accuracy so I can trust the information presented to me.
JOB TO BE DONE
Wikipedia’s job is to be the final word.
People across the world employ Wikipedia to get the final word in arguments and answer questions with accurate, indisputable information on almost any topic. Wikipedia says this – end of discussion.
In order to achieve the Job To Be Done and satisfy user’s needs, I developed a new, comprehensive set of features for Wikipedia. The features fall into three categories: Accuracy, Accountability, and Accessibility.
FEATURES
USER EXPERIENCE JOURNEY
Wikipedia’s user experience is unique in that many users don’t start at the home page or navigate through several pages during their journey; instead, the Wikipedia experience journey is more of an experience “scroll” through a specific article.
WIREFRAMES
3 Concepts for Updating the Layout of Wikipedia Articles
HIGH-FIDELITY PROTOTYPES
KILLER FEATURE
Two-Part Confidence Scores
Wikipedia feels shady because users don’t have a way to evaluate the accuracy of information in articles. Having a confidence score on all articles allows Wikipedia users to assess an article’s accuracy at a glance.
There will be two confidence scores, one powered by the AI fact-checking automatically done when an article is modified, and another given by editors.
USER TESTING
73% of users selected Option D when asked which page design they liked best
→ Users liked the “snapshot of information” at the top and found the design visually appealing
When asked which would be best to implement on all Wikipedia pages, beyond their personal preference, half the users changed their response to Option B.
→ Users liked that it was similar to the current layout, and could still be recognized as Wikipedia
→ Users thought this design would be more versatile for articles that don’t have photos or visuals
→ Users appreciated how much information was shown at the top, without needing to scroll
of users responded that having a "Confidence Score" on article pages would make Wikipedia more trustworthy.
100%
FINAL DESIGN
While I did take the users’ feedback into account, I ultimately decided that the best design for the new Wikipedia would be Option C. Despite users not selecting it as their favorite, I thought that it had the best balance of visuals while keeping information close to the top, and also showcased the new “Confidence Score” feature most prominently. Based on feedback, I updated the design to make the image at the top smaller so that more information was visible without scrolling.
Original Design
Iteration Based on User Feedback
ACCESSIBILITY IMPROVEMENTS
With Wikipedia popular internationally and available in over 331 languages, a universal font that includes a comprehensive set of characters for these languages would ensure consistent and legible text display across all versions of the site. This would not only make the site more user-friendly and maintain brand consistency but also help create a more inclusive experience for readers around the world, making it easier for everyone to enjoy and contribute to Wikipedia.
Both typefaces, Georgia and Helvetica, are available in 92 languages.
The Noto font family, in addition to being an open-source font, is available in over 1,000 languages.
In addition to updating the fonts to be more accessible, I also made the hyperlinks that are included throughout Wikipedia articles black instead of blue to create a less overwhelming reading experience, especially for neurodivergent users who may find the current system overstimulating.
Blue links can be visually distracting, breaking the flow of reading and drawing too much attention away from the main content. By using black links, the text would appear more cohesive and less cluttered, reducing visual noise and making it easier for users to focus on the information.
Goodbye, Blue Hyperlinks
Current Design: Blue links distract from content and are overstimulating, especially for neurodivergent users
New Design: In-text links are the same color as the rest of the text, and underlined to inform users of the link
the FINAL PRODUCT
DEMO
A New Look Focused on Trust
The combination of modern UI and the new Confidence Score feature help establish Wikipedia as a trustworthy source of information, allowing users to assess the accuracy of articles at a glance.
Detailed Explanation of Scores
Users are able to see why an article received the Editor and AI Confidence Scores and an explanation of what they mean. Here, users can see what impacted the score and toggle to view them in the article.
View What Impacted the Score
By showing where the article might be flawed or need additional information, Wikipedia is being transparent with users and allowing them to further assess the trustworthiness of the article.